






















And God said, “Let the waters under the heavens be gathered together into one place, and let the dry land appear.” And it was so. God called the dry land Earth, and the waters that were gathered together he called Seas. And God saw that it was good. And God said, “Let the earth sprout vegetation, plants yielding seed, and fruit trees bearing fruit in which is their seed, each according to its kind, on the earth.” And it was so. The earth brought forth vegetation, plants yielding seed according to their own kinds, and trees bearing fruit in which is their seed, each according to its kind. And God saw that it was good. And there was evening and there was morning, the third day.
Genesis 1:9-13 (ESV)
Then God said, “Let the water beneath the sky be gathered into oceans so that the dry land will emerge.” And so it was. Then God named the dry land “earth”, and the water “seas”. And God was pleased. And he said, “Let the earth burst forth with every sort of grass and seed-bearing plant, and fruit trees with seeds inside the fruit, so that these seeds will produce the kinds of plants and fruits they came from.” And so it was, and God was pleased. This all occurred on the third day.
Genesis 1:9-13 (TLB)
The Yom/Day 3 is the longest day of Genesis 1, lasting from about 3.3 billion years ago to about 410 million years ago. One reason that it is this long is that it covers two events – continents forming and then plants appearing on the continental land masses.
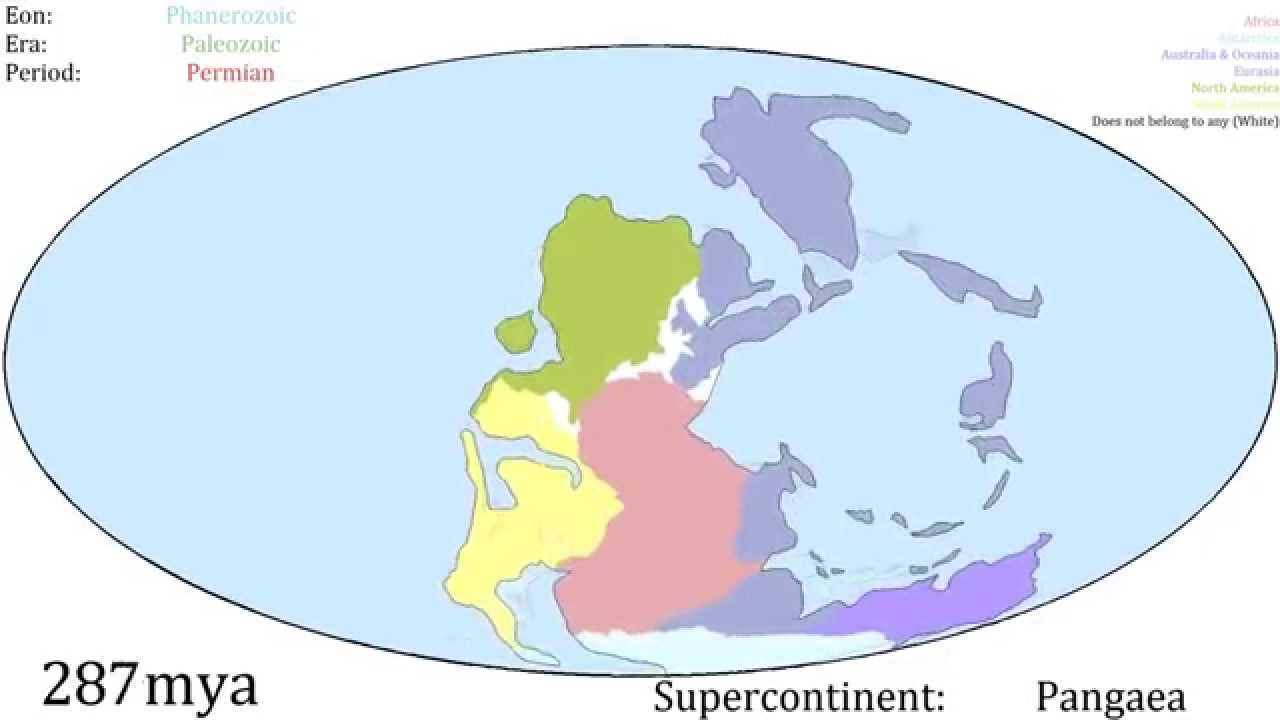
By around 4.3 billion years ago, Earth was essentially a water-covered world with little or no persistent dry land. As cooling continued between about 4.3 and 4.0 billion years ago, the magma beneath the ocean solidified into a primitive crust. These buoyant crust fragments may have risen above sea level as small islands or island chains, though they were unstable and short-lived. By around 4.0 billion years ago, the first long-lived continental nuclei—known as cratons—started to form. Land at this stage was no longer purely transient. Over the next several hundred million years, from about 3.2 to 2.5 billion years ago, continental growth accelerated. By around 2.5 billion years ago, the total volume of continental crust had reached a large fraction of its modern value. From about 2.5 to 1.8 billion years ago, the large supercontinent-scale land masses then emerged and transformed into various different shapes over time.
The transition of life from the oceans onto land occurred gradually between roughly 470 and 360 million years ago. The first plant-like colonizers were microbial communities and fungi, which helped create the earliest soils. Soon after, simple plants had structures to retain water and withstand exposure to air, allowing them to spread across moist coastal environments. These early plants fundamentally changed Earth’s surface by stabilizing soils and increasing oxygen production. By 360 million years ago (the Late Devonian period / Paleozoic Era / Phanerozoic Eon) then Earth began supporting the first true forests.

Probable Time Frame ~3300 to ~360 million years ago
- Widespread landmasses arise (3.3 to 3.0 billion years ago)
- Large, stable continental blocks (2.7 to 2.5 billion years ago)
- Supercontinent-scale landmasses (2.5 to 1.8 billion years ago)
- Microscopic Fossil Spores (cryptospores) (~470 to 445 million years ago)
- Plants with Vascular Tissue (~445 to 419 million years ago)
- Rapid Expansion and Diversification (~419–385 million years ago)
Videos about Day 3 of Creation
Playlist
4:21

42:46

36:10

32:11

21:22

10:30

44:51
| YouTube Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Continental Drift: 3.3. Billion Years | Visualization of continental drift over time. As the video states, it is difficult to talk with much certainty about details before 1 billion years ago. |
| What Was The Earth Like 1 Billion Years Ago? | What the earth was like during the "Boring Billion" years ago. |
| What Was The "Boring Billion" Really Like? | The earth from about 1800 to 800 mya, sometimes referred to the "boring billion" year period. |
| What Was The Earth Like 2 Billion Years Ago? | History of investigations about what the earth was like 2 bya. |
| Were Volcanoes The Key To Life? | Covers much of earth history and includes an overview of the uniqueness of plate tectonics. |
| The World Before Plate Tectonics< | Covers how and why plate tectonics started. |
| How Flowering Plants Conquered the Earth | Covers the plant evolution from about 800 mya |

